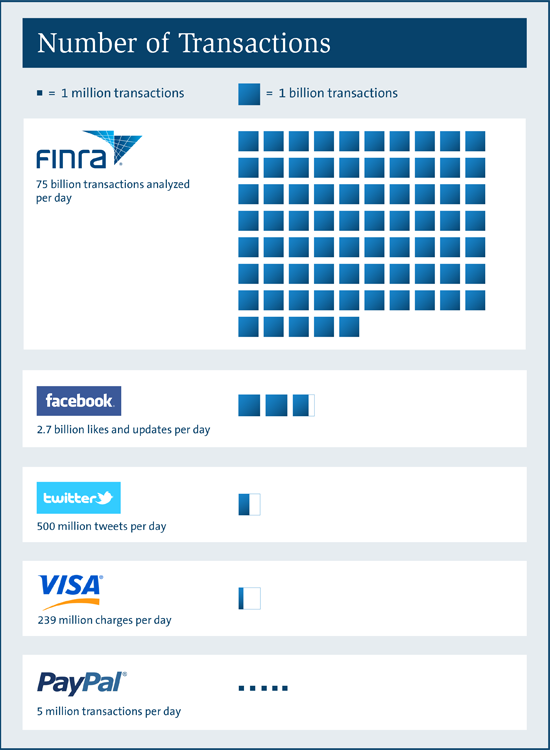
What Is The FINRA? Understanding The Role And Importance Of The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority
FINRA, or the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, is a crucial organization in the United States that plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity of the financial markets and protecting investors. Established in 2007, FINRA operates as a self-regulatory organization (SRO) tasked with overseeing the activities of brokerage firms and securities firms. Its mission is to maintain fairness, transparency, and trust in the financial industry, which directly impacts millions of investors across the country.
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the need for robust regulation becomes increasingly important. FINRA's primary objective is to enforce rules and regulations that govern the conduct of financial professionals, ensuring they adhere to ethical standards and act in the best interests of their clients. This regulatory framework helps safeguard investors from fraudulent practices, misleading information, and unethical behavior.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the functions, structure, and significance of FINRA. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of what FINRA is, its role in the financial industry, and why it matters to investors, brokers, and financial professionals alike.
Read also:Amc Johnson City 14 Prices A Comprehensive Guide To Your Movie Experience
Table of Contents
- History of FINRA
- Mission and Objectives of FINRA
- Structure and Governance of FINRA
- Regulatory Functions of FINRA
- Enforcement and Compliance
- Investor Protection Initiatives
- Rules and Standards Set by FINRA
- Technology and Innovation in FINRA
- Challenges Facing FINRA
- The Future of FINRA
History of FINRA
The origins of FINRA can be traced back to the consolidation of two major organizations: the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) Regulation and the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD). In 2007, these entities merged to form FINRA, creating a unified regulatory body with a broader scope and more comprehensive oversight capabilities.
This merger was driven by the need for a more efficient and effective regulatory framework to address the complexities of the modern financial industry. By combining the resources and expertise of both organizations, FINRA was able to streamline operations, reduce redundancies, and enhance its ability to protect investors and maintain market integrity.
Key Milestones in FINRA's Development
- 2007: Official establishment of FINRA through the merger of NYSE Regulation and NASD.
- 2010: Introduction of the Office of Fraud Detection and Market Intelligence to combat fraudulent activities.
- 2015: Launch of the FINRA Investor Education Foundation to promote financial literacy among the public.
Mission and Objectives of FINRA
FINRA's mission is to ensure the integrity of the financial markets and protect investors through effective regulation and oversight. This mission is supported by a set of core objectives that guide its operations and decision-making processes.
One of the primary objectives of FINRA is to maintain high standards of ethical behavior and professional conduct among financial professionals. This is achieved through the establishment of comprehensive rules and regulations that govern the activities of brokerage firms and securities firms. Additionally, FINRA is committed to fostering transparency and fairness in the financial markets, ensuring that all participants have access to accurate and timely information.
Core Objectives of FINRA
- Protect investors from fraudulent practices and unethical behavior.
- Ensure the integrity and fairness of the financial markets.
- Promote transparency and accountability in the financial industry.
Structure and Governance of FINRA
FINRA operates as a self-regulatory organization (SRO) under the supervision of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Its governance structure is designed to ensure accountability, transparency, and independence in its operations.
The organization is governed by a Board of Governors, which consists of representatives from the financial industry, public members, and FINRA staff. This diverse composition ensures that FINRA's policies and decisions reflect a balanced perspective, taking into account the interests of all stakeholders.
Read also:Perfect Temperature For Mediumrare Steaks A Comprehensive Guide
Key Components of FINRA's Governance Structure
- Board of Governors: Responsible for setting strategic priorities and overseeing FINRA's operations.
- Executive Management: Implements policies and manages day-to-day operations.
- Committees: Focus on specific areas such as enforcement, investor protection, and rulemaking.
Regulatory Functions of FINRA
FINRA's regulatory functions encompass a wide range of activities aimed at ensuring compliance with its rules and regulations. These functions include registration and licensing, examination and surveillance, and enforcement of rules and standards.
Through its registration and licensing processes, FINRA ensures that only qualified and ethical professionals are authorized to operate in the financial industry. Examination and surveillance activities help detect and prevent fraudulent practices, while enforcement actions are taken against individuals or firms that violate FINRA's rules.
Examples of FINRA's Regulatory Functions
- Conducting regular audits of brokerage firms to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Monitoring trading activities to detect suspicious patterns or anomalies.
- Taking disciplinary actions against firms or individuals found to be in violation of rules.
Enforcement and Compliance
Enforcement is a critical component of FINRA's regulatory framework. The organization has a dedicated enforcement division responsible for investigating violations and imposing appropriate sanctions. These sanctions can range from fines and suspensions to permanent bans, depending on the severity of the offense.
FINRA also places a strong emphasis on compliance, providing resources and guidance to help firms and professionals adhere to its rules and regulations. This proactive approach helps prevent violations and promotes a culture of integrity and accountability within the financial industry.
Enforcement Statistics
- In 2022, FINRA imposed over $50 million in fines and restitution to harmed investors.
- More than 1,000 disciplinary actions were taken against firms and individuals.
Investor Protection Initiatives
Protecting investors is at the heart of FINRA's mission. The organization has implemented numerous initiatives aimed at enhancing investor protection and promoting financial literacy. These initiatives include educational programs, complaint resolution services, and resources for investors to make informed decisions.
FINRA's Investor Education Foundation plays a key role in promoting financial literacy by providing free resources and tools to help individuals better understand the financial markets and investment products.
Investor Protection Resources
- BrokerCheck: A tool that allows investors to research the background of brokers and brokerage firms.
- Investor Alerts: Regular updates on potential risks and scams in the financial industry.
- Financial Literacy Programs: Workshops and resources to educate the public about investing and personal finance.
Rules and Standards Set by FINRA
FINRA has established a comprehensive set of rules and standards that govern the conduct of financial professionals and firms. These rules cover a wide range of areas, including sales practices, trading activities, and financial operations.
Some of the key rules include the suitability rule, which requires brokers to recommend investments that are appropriate for their clients' financial situations, and the fair dealing rule, which mandates that brokers act in the best interests of their clients.
Examples of FINRA Rules
- Suitability Rule: Brokers must recommend investments that are suitable for their clients' needs and circumstances.
- Fair Dealing Rule: Brokers must act in the best interests of their clients and avoid conflicts of interest.
Technology and Innovation in FINRA
FINRA has embraced technology and innovation to enhance its regulatory capabilities and improve efficiency. The organization utilizes advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence to monitor market activities and detect potential violations.
In addition, FINRA has developed innovative tools and platforms to facilitate communication and collaboration with industry participants. These technological advancements have enabled FINRA to stay ahead of emerging risks and challenges in the financial industry.
Technological Advancements in FINRA
- Use of artificial intelligence to analyze large datasets and identify patterns of suspicious activity.
- Development of digital platforms for filing complaints and accessing resources.
Challenges Facing FINRA
Despite its successes, FINRA faces several challenges in fulfilling its mission. One of the primary challenges is keeping pace with the rapid evolution of the financial industry, particularly in areas such as fintech and digital assets. Additionally, FINRA must balance the need for strict regulation with the desire to foster innovation and growth in the industry.
Another challenge is addressing the increasing complexity of financial products and services, which can make it difficult for investors to fully understand the risks and benefits involved. FINRA must continue to adapt and evolve to meet these challenges and ensure the continued protection of investors.
The Future of FINRA
Looking ahead, FINRA is poised to play an even more critical role in the financial industry as it continues to address emerging challenges and opportunities. The organization is committed to leveraging technology and innovation to enhance its regulatory capabilities and improve investor protection.
As the financial landscape becomes increasingly complex, FINRA's ability to adapt and evolve will be crucial in maintaining the integrity and fairness of the financial markets. By staying ahead of emerging trends and risks, FINRA will continue to serve as a trusted guardian of investor interests and market integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FINRA is a vital organization that plays a crucial role in regulating the financial industry and protecting investors. Through its comprehensive regulatory framework, enforcement actions, and investor protection initiatives, FINRA ensures the integrity and fairness of the financial markets.
We encourage readers to stay informed about FINRA's activities and take advantage of the resources and tools it provides. By doing so, investors can make more informed decisions and protect their financial interests. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below and explore other articles on our site for more insights into the world of finance.